Day 13 - Understand the power of Polymorphism and Abstraction in Python
Today we will understand two of the most important concepts of Object Oriented Programming (OOP) – Polymorphism and Abstraction. Both of these principles make algorithmic trading software more powerful and flexible. Especially when you are working on crypto trading strategies in USA or quantitative analysis for trading in Singapore, these concepts can take your skills to new heights.
Polymorphism – One Function, Many Ways
Polymorphism means “one function that works in many ways.” Polymorphism in Python can be divided into three parts:
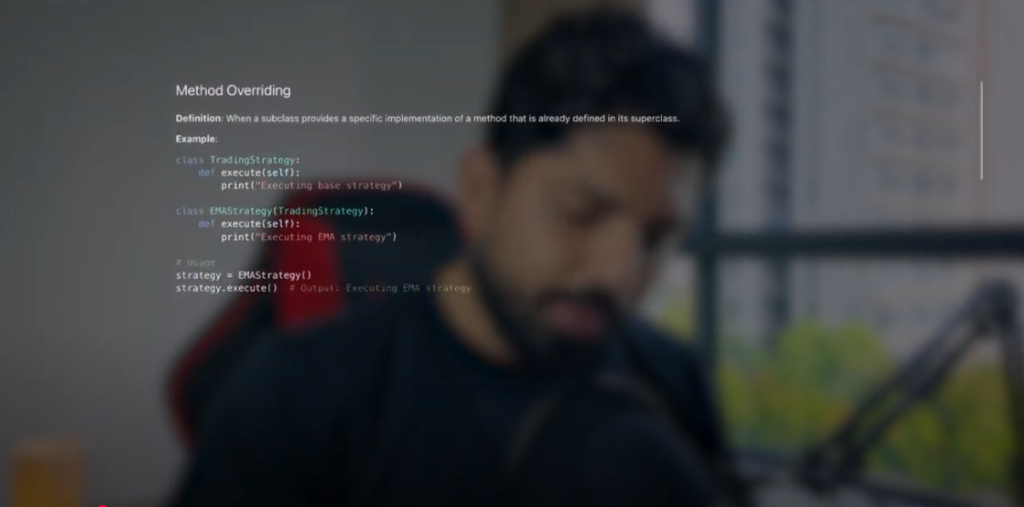
Method Overriding – Customizing the Parent Method
When a child class redefines the method of the parent class in its own way, it is called method overriding.
class Strategy:
def execute(self):
print(“Parent Strategy”)
class EMAStrategy(Strategy):
def execute(self):
print(“Child EMA Strategy”)
Now if we create an object of EMAStrategy and call execute(), then the method of the child class will run. This is Method Overriding.
Method Overloading – One Method, Multiple Behaviors
Python does not support method overloading directly like Java. But Python has handled it in a smart way – through default arguments and variable-length arguments.
class Maths:
def area(self, a1, a2=0):
if a2 == 0:
return 3.14 * a1 * a1 # Circle
else:
return a1 * a2 # Rectangle
If only one argument is given then it will return the area of a Circle.
If two arguments are given then it will return the area of a Rectangle.
This is the smart approach of Method Overloading in Python.
Operator Overloading – Redefine Operators as per your requirement
In Python, you can redefine operators like +, -, * as per your requirement. This is called Operator Overloading.
a = “Hello”
b = “World”
print(a + b) # Output: HelloWorld
Here the + operator is concatenating the string. If the same operator is used on numbers, it will perform addition.
This flexibility is called Operator Overloading.
Watch this Day 13 video tutorial
Day 13: Polymorphism & Abstraction | OOP Part – 5
![]()

