Algorithmic Trading with Python: A Revolutionary Journey
In today’s digital age, Algorithmic Trading with Python has completely transformed the financial markets. Traders can now automate their decisions, making trading faster, more accurate, and profitable. Whether you want to learn Crypto Trading Strategies or are looking for the Best Algorithmic Trading Software in the US, automation can multiply your trading potential.
The demand for Quantitative Analysis for Trading is also constantly increasing in Singapore, where traders are developing their trading systems in a more scientific way. In this guide, we will understand everything from Freqtrade Strategy Setup to advanced concepts of Python like Nested Functions and First-Class Functions.
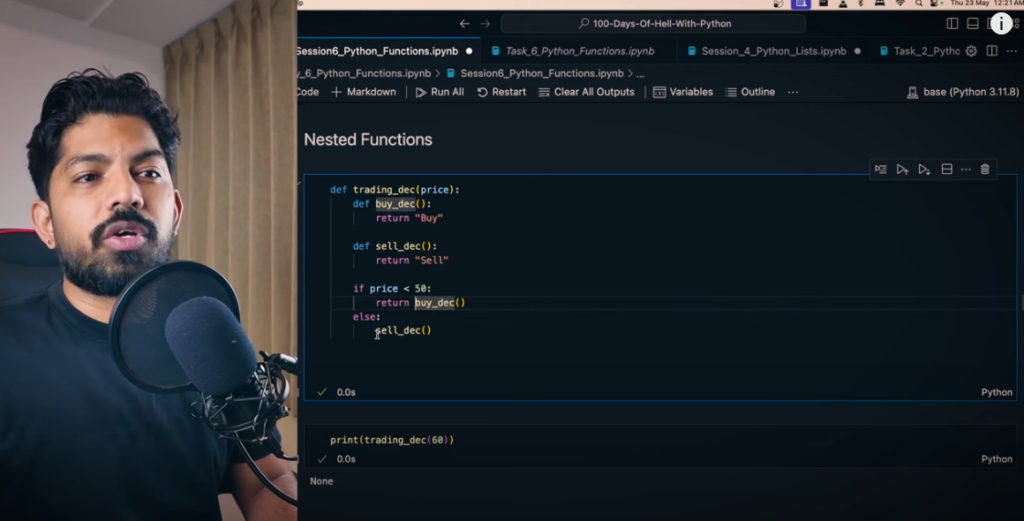
What are Nested Functions in Python?
Nested Functions means – another function inside a function. Just like we saw Nested Loops in Lists and Loops, in Python you can also create other functions inside a function.
Example:
def trading_decisions(price):
def buy_decision():
return “Buy”
def sell_decision():
return “Sell”
if price < 50:
return buy_decision()
else:
return sell_decision()
print(trading_decisions(40)) # Output: Buy
print(trading_decisions(60)) # Output: Sell
In this example, we have created a main function trading_decisions and inside it two nested functions – buy_decision() and sell_decision(). Based on the price, the corresponding decision (Buy/Sell) is taken.
Why are functions first-class citizens in Python?
One of the major reasons that makes Python powerful is that functions are considered first-class citizens in it. This means that:
- Functions can be assigned to variables
- Functions can be passed as arguments
- Functions can be returned from a function
- Functions can be stored in data structures such as lists, tuples, dictionaries
- Functions can be given attributes
Utility:
- It lets you create higher-order functions
- Callbacks and event handlers are possible in GUIs
- It is very helpful in functional programming
- It becomes easy to handle dynamic behavior
- Functions are also objects – with examples
Everything in Python is an object – even functions. Let’s see an example:
def trading_logs():
pass
print(type(trading_logs)) # Output: <class ‘function’>
print(id(trading_logs)) # Memory Address
Here trading_logs has the type ‘function’, which indicates that it is also an object.
Assigning a function to a variable in Python
You can also assign a function to a new variable and call the function from it. For example:
def trading_logs(price1, price2):
return price1 + price2
sum_prices = trading_logs # Assigning a function to a variable
print(sum_prices(2, 3)) # Output: 5
This feature helps you to create modular and flexible code, which is later useful in large Algo Trading projects.
Uses of Python Functions in Algo Trading
Functions are used in various aspects in Algo Trading:
- Signal Generation: Custom Functions for Buy/Sell signals
- Strategy Building: Like creating custom strategies in Freqtrade
- Risk Management: Handling Stop Loss, Take Profit etc. with functions
- Backtesting: Function-Based Testing to check the performance of the strategy
To understand Algo Trading, you need to have a deep understanding of functions – and Python proves to be the best tool for this.
Practice: MCQs, Tasks and Mini Projects
At the end of this blog, you are advised to:
Solve MCQs to strengthen the concepts
Do Algo Trading based tasks so that you can implement the strategy with code
Work on a Mini Project – It connects your skills to real world applications
Doubts? Join the Community
If you have any doubts, you can reach out to us on:
- Discord
- Telegram
- YouTube Comments
Our community is always ready to help.
Understanding Python Functions is a must to succeed in the world of Algo Trading. Be it Nested Functions or First-Class Functions, every concept improves your trading skills. Practice, experiment and keep learning – that is the real power of Algo Trading with Python.
Watch this Day 8 video tutorial
Day 8: Python Functions Part – 2
![]()

